A Guide to Food Glycemic Index
For a very long time, doctors considered that only sweet foods influenced blood sugar levels. They distinguished between two types of carbohydrates: simple carbohydrates or simple sugars, which are quickly digested by the body and raise blood glucose levels quickly, and complex carbohydrates or complex sugars, which are slowly digested and raise blood glucose levels only gradually.
Since then, the work carried out by researchers has shown that these considerations were wrong. All foods can influence blood sugar levels, depending on their glycemic index.
Since then, other criteria have been established that provide information on the quality of food in connection with diabetes, such as glycemic load, carbohydrate meter, insulin or insulin index.
What is the glycemic index of foods?
The glycemic index is used to classify foods according to their impact on the rise in blood sugar levels as soon as they are ingested. This criterion is very useful for diabetic patients to balance their diet.
Principle of the glycemic index
The glycemic index of a food evaluates its ability to raise blood sugar levels more or less quickly by comparing it with an equivalent amount of pure glucose, whose glycemic index has been taken as 100.
For instance, a glycemic index of 70 means that the food has a glycemic effect equal to 70% of that of glucose; a glycemic index of 20 corresponds to 20% of that of glucose, etc.
For example:
– the higher the glycemic index, the higher and faster the blood sugar level rises;
– the lower it is, the slower and to a lesser extent the blood sugar rises, according to a flattened curve spread out over time.
Glycemic index during a meal
The glycemic index of a meal is the average of the glycemic indexes of its various components: eating carbohydrate portions in the middle of a meal always raises blood sugar levels less than an isolated snack. In addition, the glycemic index of food varies:
– according to the type of cooking: the glycemic index of pasta cooked al dente (lightly cooked, still crunchy) is 32 to 38, whereas it can exceed 50 if the pasta is very cooked;
– according to food or drink combinations: the glycemic index of white bread (70) increases if you drink water while eating it, whereas it decreases if you spread it with butter;
– in the presence of proteins, fats, vegetable fibres which lower the glycemic index.
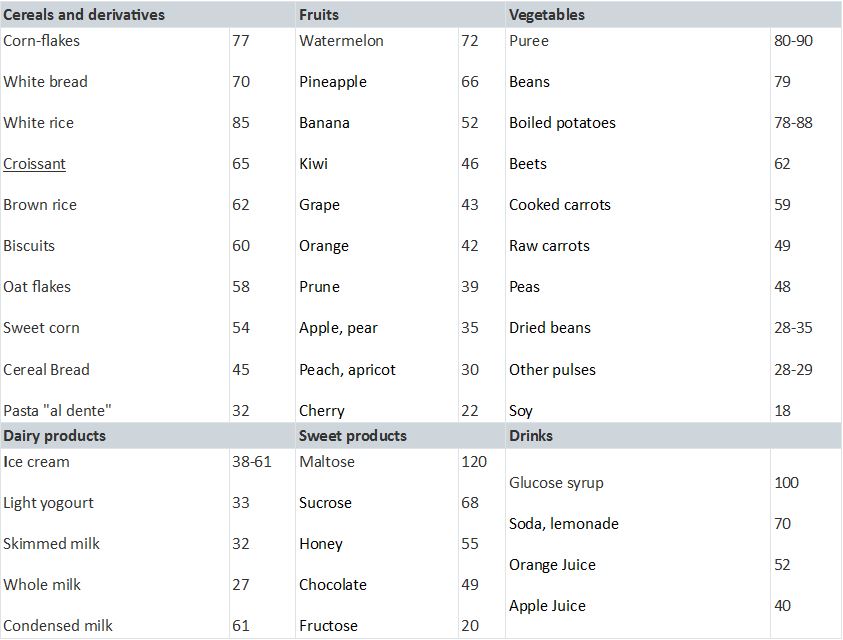
Average values of the glycemic index of foodstuffs

The following table shows the glycemic index of the main foods:
Scientific studies on the glycemic index (GI) have completely changed the old conception based on the distinction between fast and slow sugars. It is now recognized that:
– white bread or rice raise blood sugar levels as fast as sucrose (table sugar) and much faster than honey;
– the majority of fruits rich in fructose, previously not recommended for diabetics, have a low GI and have little effect on blood sugar levels;
– Various sweet-tasting desserts have less effect on blood sugar levels than potatoes.
Why monitor the glycemic index?
Diabetics or not, everyone should monitor their diet and manage their carbohydrate intake. Carbohydrates are essential to the functioning of the body, they must represent an important part of daily food intake, but also be consumed intelligently.
The interest of the glycemic index for diabetics
The main application of the glycemic index of foods (GI) is for diabetics. Diabetics’ diets should contain as many carbohydrates as those of non-diabetics, but they should avoid an excessive increase in their blood sugar levels.
From this point of view, foods are classified according to their GI:
– foods with a GI higher than 75 should be avoided (very high GI);
– foods with a GI between 50 and 75 are to be limited (high GI);
– foods with a GI of less than 50 are to be preferred to ensure carbohydrate intake (medium or low GI).
In practice, a diabetic must:
– eat wholemeal or cereal bread instead of white bread;
– prefer slow-cooking wholemeal or basmati rice to quick-cooking rice;
– cook pasta al dente;
– give a larger portion to pulses and legumes, except beans;
– give preference to European fruits over tropical fruits;
– always mix high GI starchy foods (potato, rice) with high fibre vegetables.
Diabetics who select medium or low GI foods have lower blood sugar levels after meals, which can avoid additional insulin injections. His or her diabetes is more stable and better balanced.
The interest of the glycemic index for non-diabetics
A balanced diet is essential for good health. As a general rule, foods with a GI above 75 should be avoided.
Eating foods with a medium or low GI is the best way to prevent hypoglycemia because carbohydrates pass more slowly through the bloodstream. It also limits feelings of hunger and the need to snack.
Good to know: Reducing the risk of hypoglycemia is as important for diabetics as it is for endurance athletes or strength workers.
Find out more in the link: What is the glycemic load?




1 Response
[…] A Guide to Food Glycemic Index […]