A Comprehensive Guide To Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, a bacterial infection primarily transmitted through tick bites, has become a growing concern in many parts of the world. It’s a complex illness with a wide range of symptoms that can make it challenging to diagnose and treat. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of Lyme disease, from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Whether you’re looking to educate yourself or seeking answers for a loved one, this article aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of Lyme disease.
What Causes Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. These ticks are most prevalent in wooded and grassy areas.
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Lyme disease can manifest in various ways and often progresses through three stages:
a. Early Stage:
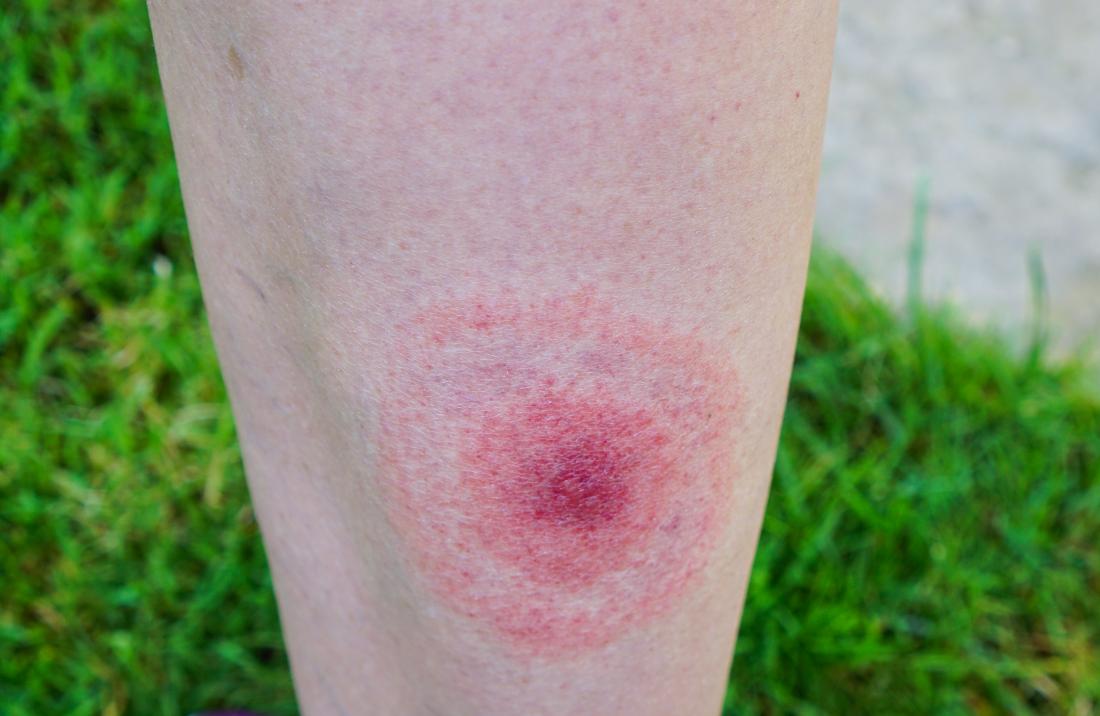
Erythema migrans (EM) Rash: The hallmark sign of Lyme disease is a circular, red rash resembling a bull’s-eye that appears within 3-30 days after a tick bite.
Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
b. Intermediate Stage:
Neurological Symptoms: These may include nerve pain, Bell’s palsy (facial muscle weakness), and shooting pains.
Heart Involvement: Palpitations and chest pain in some cases.
c. Late Stage:
Arthritis: Severe joint pain and swelling, particularly in the knees.
Neurological Complications: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes.
Heart and Nervous System Issues: Rare but serious complications like heart block or inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Treatment
Antibiotics: The primary treatment for Lyme disease involves a course of antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic, dosage, and duration depends on the stage and severity of the disease.
Early Treatment: Lyme disease is most effectively treated in its early stages. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime.
Late or Complicated Cases: Intravenous antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone, may be necessary for severe or persistent cases. In such cases, treatment may take several weeks to months.
Pain Management: For those experiencing pain, over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatories can be used.
Prevention
Tick Avoidance: Minimize your risk of Lyme disease by:
- Wearing long sleeves and pants when in wooded or grassy areas.
- Using tick repellent.
- Conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
- Showering within two hours of being outdoors to wash away unattached ticks.
Tick Removal: If you find a tick, remove it promptly using fine-tipped tweezers. Grasp the tick close to the skin’s surface and pull upward with steady, even pressure.
Tick-Proof Your Yard: Keep your yard clean and free from tall grass, leaf litter, and other tick-friendly environments. Consider using tick-control products.
Vaccination: While there is no human Lyme disease vaccine currently available, research continues in this area.
Lyme Disease and Co-Infections
Lyme disease can sometimes be accompanied by other tick-borne infections, known as co-infections. These may include Anaplasmosis, Babesiosis, and Ehrlichiosis. Co-infections can complicate diagnosis and treatment, so it’s essential to be aware of the possibility and seek medical attention if you suspect multiple tick-borne illnesses.
Chronic Lyme Disease Controversy
Lyme disease can become a chronic condition for some individuals, leading to ongoing symptoms even after standard treatment. This has sparked debate within the medical community about the existence of chronic Lyme disease. Some argue that lingering symptoms may result from autoimmune responses triggered by the initial infection, while others believe it is due to persistent infection. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to address ongoing symptoms and explore treatment options tailored to your specific situation.
Support and Coping
Lyme disease is a complex and potentially debilitating illness that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Early recognition of symptoms, tick prevention, and tick removal are essential steps in reducing your risk of contracting this disease. If you or a loved one suspects Lyme disease, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing and treatment. As research continues, advancements in Lyme disease diagnosis and treatment offer hope for improved outcomes in the future. Stay informed, take precautions, and prioritize your health to reduce the impact of Lyme disease on your life.